Managing Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to a Healthier Life

Empowering You to Take Control of Your Diabetes Journey
Living with diabetes requires a thoughtful and proactive approach to health. Whether you've recently been diagnosed or have been managing diabetes for some time, this guide is designed to provide practical insights, tips, and encouragement on your journey to better health.
Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar (glucose) levels. This can occur due to insufficient insulin production or the body’s inability to effectively use insulin.
The common types are Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 is usually diagnosed in childhood, Type 2 is more common in adults, and gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy.
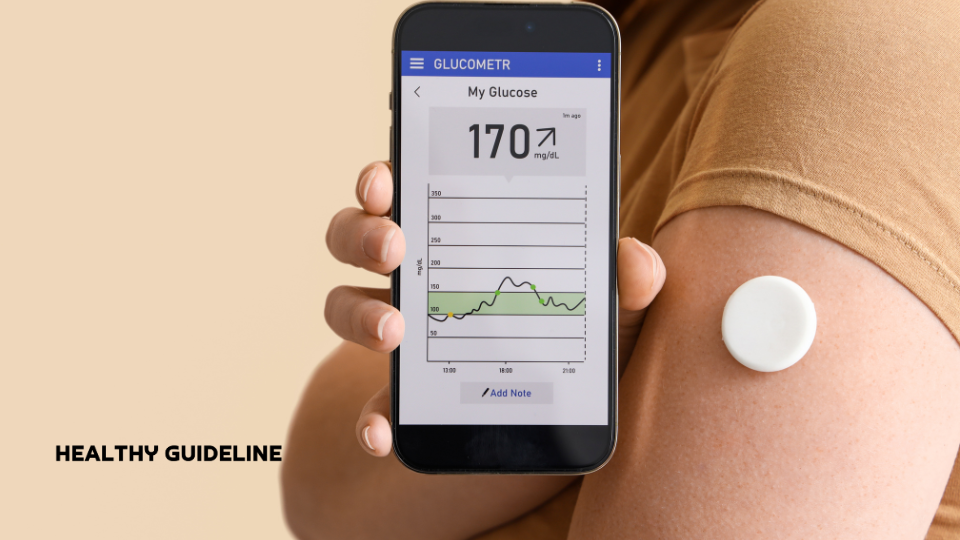
Diabetes is typically diagnosed through blood tests measuring fasting blood sugar levels, oral glucose tolerance tests, or HbA1c levels.
Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but Type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. In diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1) or doesn’t use it effectively (Type 2). Insulin therapy may be necessary for management.
Management includes monitoring blood sugar levels, adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, taking prescribed medications, and, if necessary, using insulin.
The HbA1c test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It is typically done every 3-6 months, depending on individual circumstances.
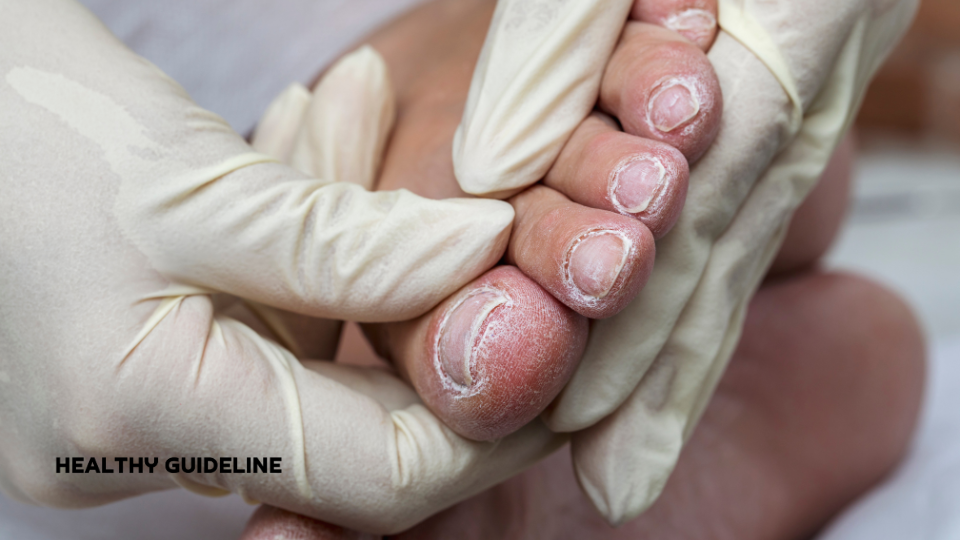
Yes, diabetes can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems. Proper management reduces the risk of complications.
There is no one-size-fits-all diet, but a balanced diet with controlled portions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is essential. Consultation with a dietitian is recommended.
Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote overall well-being. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
Yes, the stress of managing diabetes can impact mental health. Adopting stress-management techniques and seeking support are important.
Limit foods high in refined sugars and carbohydrates. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables.
Type 1 diabetes has no cure, but Type 2 diabetes can be managed effectively, and sometimes remission is possible with lifestyle changes.
Yes, diabetes during pregnancy (gestational diabetes) requires careful management to avoid complications for both the mother and baby.
Warm up and cool down, listen to your body, wear appropriate attire, use proper form, and stay hydrated.
Stress hormones can raise blood sugar levels. Managing stress through relaxation techniques is beneficial.
Moderation is key. Consult with a healthcare provider to understand how alcohol may affect blood sugar and interact with medications.
Most artificial sweeteners are safe in moderation. It’s crucial to consider overall diet and consult with a healthcare professional.
DKA is a severe complication of diabetes, more common in Type 1. It results from a lack of insulin, leading to the production of ketones.
Yes, diabetes can lead to eye problems such as diabetic retinopathy. Regular eye exams are essential.
The frequency of monitoring depends on individual circumstances. It may range from multiple times a day to less frequently.
Fasting may require adjustments to medication and careful monitoring. Consult with a healthcare provider before attempting fasting.
Uncontrolled diabetes may impact fertility. Maintaining good blood sugar control is crucial for reproductive health.
Neuropathy is nerve damage that can result from diabetes. It can lead to pain, tingling, or numbness in the extremities.
Yes, diabetes is a risk factor for heart disease. Managing blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol is essential for heart health.
Stress itself doesn’t cause diabetes, but it can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. Managing stress is important for overall well-being.
Yes, with proper planning. Ensure an adequate supply of medications, snacks, and monitoring tools. Consult with a healthcare provider before traveling.
Uncontrolled diabetes may weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
While some studies suggest benefits, it’s not a substitute for diabetes management. Consult with a healthcare provider before adding supplements.
Consume a fast-acting source of glucose, such as juice or candy, to raise blood sugar. Seek medical attention if symptoms persist.
Remember, living well with diabetes is not just about managing numbers; it's about embracing a lifestyle that nurtures your overall well-being. Stay committed to your personalized care plan, prioritize regular check-ups, and lean on the support of healthcare professionals and loved ones. Every effort you make towards a healthier lifestyle is a victory in itself. Embrace the journey, celebrate your successes, and never hesitate to seek guidance. With the right care and mindset, you have the power to lead a fulfilling and vibrant life despite diabetes. Your health is a priority, and you're not alone on this path – together, we navigate towards well-being."